How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone components, explore various flight modes, and equip you with the knowledge to capture stunning aerial footage.
Prepare to take flight with confidence!
This guide is designed to be accessible to both beginners and experienced pilots. Whether you’re a complete novice or looking to refine your existing skills, you’ll find valuable insights and practical tips within these pages. We will cover essential safety protocols, troubleshooting common issues, and best practices for maintaining your drone’s longevity. By the end, you’ll be ready to navigate the skies with skill and responsibility.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and efficient operation. This section will Artikel the key parts of a typical drone, define common terminology, and provide troubleshooting tips for each component.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Each plays a vital role in its overall performance and safety.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. Brushless motors are commonly used for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the “brain” of the drone, receiving commands from the remote controller and managing the motors to maintain stability and execute flight maneuvers. It integrates data from various sensors (e.g., gyroscope, accelerometer, barometer).
- Battery: Provides the power source for all drone components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are standard due to their high energy density and lightweight nature.
- GPS Module (optional but common): Enables precise positioning and autonomous flight functions such as waypoint navigation and return-to-home (RTH).
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos, often stabilized with a gimbal for smoother footage.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: This system allows the pilot to control the drone wirelessly. The transmitter sends commands, and the receiver interprets and relays them to the flight controller.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a consistent altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera, reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth footage.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- Waypoint Navigation: A flight mode where the drone follows a pre-programmed path of GPS coordinates.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor individually, allowing for precise control.
- Firmware: The software that runs the drone’s flight controller.
Drone Component Troubleshooting
This table provides troubleshooting tips for common drone components and their associated issues.
| Component | Function | Troubleshooting Tips | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust | Inspect for damage, replace if bent or cracked | Bent, cracked, unbalanced |
| Motors | Power propellers | Check connections, inspect for overheating | Overheating, motor failure |
| Flight Controller | Controls flight | Recalibrate, check firmware, ensure secure connections | Unresponsive, erratic flight, loss of control |
| Battery | Provides power | Check voltage, replace if damaged or swollen | Low voltage, rapid discharge, swelling |
| GPS Module | Provides location data | Ensure clear sky view, check GPS signal strength | Weak signal, GPS loss |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. This involves checking the drone’s physical condition, calibrating components, and verifying battery levels.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, systematically follow this checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage (propellers, arms, body).
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Verify GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Test the motors and propellers for proper function.
- Check radio control connection and responsiveness.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Select an appropriate flight location with ample space and clear obstacles.
Battery Level and Calibration
Battery level is critical for flight duration and safety. Insufficient charge can lead to unexpected power loss mid-flight. Regular calibration of the compass and IMU ensures accurate sensor readings, contributing to stable flight performance. These calibrations usually involve specific procedures within the drone’s software or app.
Visual Inspection for Damage
A visual inspection before each flight is vital for identifying any potential issues. Look for cracks, bends, or loose components on the propellers, arms, body, and landing gear. Check all connections for security and signs of damage. A damaged drone is a safety hazard and should not be flown.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are paramount for preventing accidents. These procedures should account for wind conditions and ensure a smooth transition between ground and flight.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
For a safe takeoff, begin with a gentle throttle increase, allowing the drone to lift slowly and steadily. Maintain control throughout the ascent. For landing, gradually decrease the throttle, ensuring a slow and controlled descent. Avoid sudden movements or abrupt changes in throttle.
Wind Conditions
Wind can significantly affect takeoff and landing. In windy conditions, position the drone into the wind to minimize drift. For takeoff, a slight increase in throttle may be needed to counteract the wind. During landing, be prepared for potential wind gusts and make necessary adjustments to maintain control.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Flowchart
This flowchart visually represents the steps involved in a safe takeoff and landing sequence:
(Illustrative description: The flowchart would show a sequence of steps, starting with pre-flight checks, moving to takeoff (gentle throttle increase, steady ascent), hovering, and then landing (gentle throttle decrease, controlled descent), finally ending with post-flight checks.)
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This involves mastering the use of control sticks and understanding different flight modes.
Control Stick Functions
Most drones use two control sticks: one for throttle and yaw, and the other for pitch and roll.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
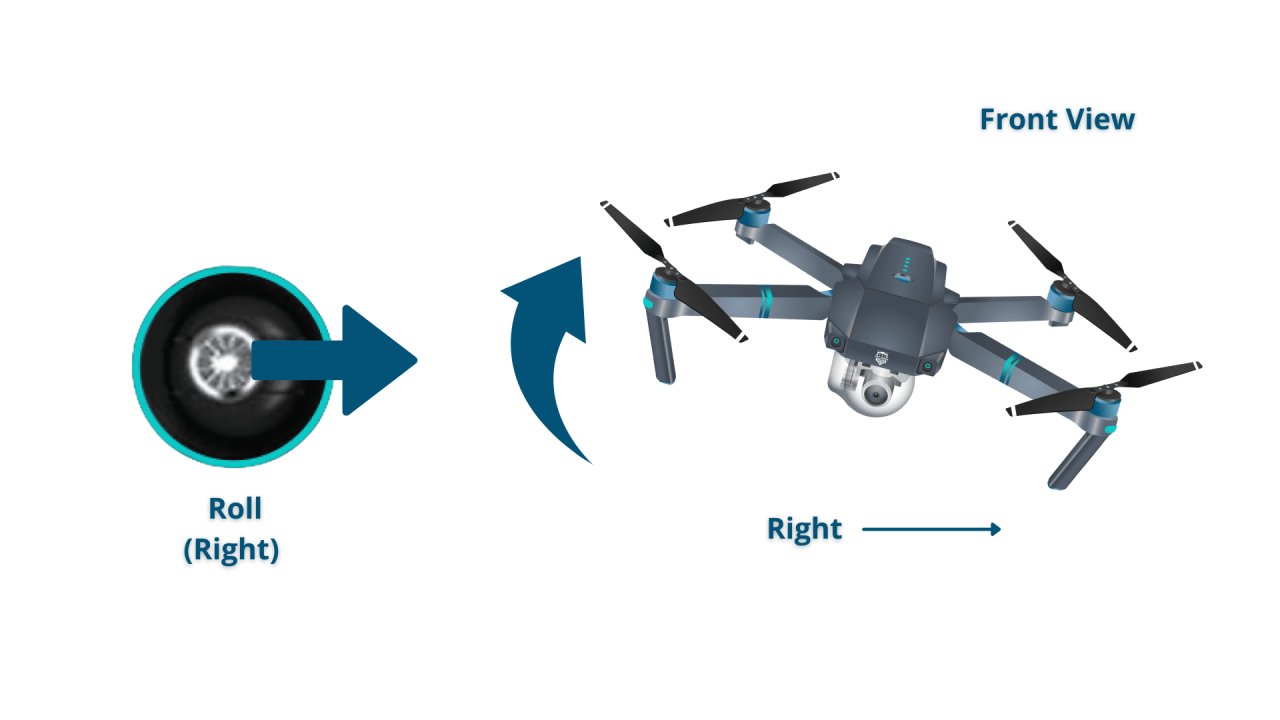
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right (sideways).
Basic Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area:
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone left or right.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes to cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Increases speed and responsiveness for more experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for more stable flight and features like RTH.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enhance a pilot’s capabilities and allow for more creative aerial photography and videography.
Waypoint Navigation and Filming
Waypoint navigation allows for pre-planned flight paths, ideal for capturing cinematic shots. Filming techniques involve understanding camera settings, composition, and movement to create visually appealing content.
GPS for Autonomous Flight

Setting up GPS for autonomous flight typically involves enabling the GPS feature in the drone’s software or app and ensuring a strong GPS signal. The drone then uses this signal to maintain its position and follow pre-programmed flight paths.
Tips for Improved Flight Stability and Precision
Maintaining stability and precision requires practice and understanding of environmental factors. Smooth control inputs and awareness of wind conditions are key elements.
- Practice smooth, controlled movements of the control sticks.
- Be aware of wind conditions and adjust your flying accordingly.
- Utilize features like altitude hold and GPS assistance.
- Regularly calibrate your drone’s sensors.
Drone Camera Operation and Settings
Understanding drone camera settings allows for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This involves adjusting resolution, frame rate, ISO, and other parameters.
Camera Settings
Common camera settings include:
- Resolution: Determines the image size (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- Frame Rate: Determines the number of frames per second (fps), impacting smoothness of video.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light, affecting brightness and noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media, How to operate a drone
Capturing high-quality aerial media requires understanding the interplay of these settings and adapting them to lighting conditions and desired aesthetic.
Camera Setting Comparison

This table compares different camera settings and their effects on image quality:
| Setting | Low Value | High Value | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 720p | 4K | Higher resolution yields sharper, more detailed images. |
| Frame Rate | 24 fps | 60 fps | Higher frame rate results in smoother video. |
| ISO | 100 | 3200 | Higher ISO allows for shooting in low light but increases noise. |
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation requires adherence to safety guidelines and legal regulations. This includes respecting airspace restrictions and maintaining privacy.
Safety Considerations
Always prioritize safety. Fly in open areas away from people and obstacles. Be mindful of wind conditions and battery life. Never fly beyond your skill level.
Local and National Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Research and comply with all local and national laws governing drone operation. This typically involves registration, licensing, and airspace restrictions.
Privacy and Restricted Airspace
Respect others’ privacy. Avoid flying over private property without permission. Be aware of restricted airspace, such as airports and military bases. Many countries have apps and websites that show restricted airspace.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone problems and offers solutions to help you resolve them effectively.
Solutions for Common Problems
Common problems and their solutions:
- Low Battery Warning: Land immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly to an area with a clear view of the sky or retry calibration.
- Motor Malfunctions: Check motor connections, inspect for damage, and replace if necessary.
- Unexpected Loss of Control: Land immediately and investigate potential causes (e.g., interference, low battery).
Mid-Flight Malfunctions
In case of a mid-flight malfunction, prioritize safety. Attempt a controlled landing if possible; if not, try to guide the drone to a safe location away from people and obstacles.
Troubleshooting Guide
This guide summarizes common issues and their solutions:
- Problem: Propeller damage. Solution: Inspect and replace damaged propellers.
- Problem: Low battery warning. Solution: Land immediately and recharge the battery.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Solution: Find a location with a clear view of the sky, recalibrate GPS.
- Problem: Erratic flight. Solution: Check for loose connections, recalibrate sensors, update firmware.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Proper maintenance and storage are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing damage.
Cleaning and Maintaining Components
Regularly clean the drone’s components, especially the propellers and body, using a soft cloth and mild detergent. Inspect for any wear and tear and replace damaged parts.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and successful flights.
Storage Methods
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use a protective case or bag to prevent damage during transportation and storage.
Extending Battery Lifespan
Store LiPo batteries at a partially charged state (around 30-50%) and in a cool, dry place. Avoid overcharging or deep discharging.
Emergency Procedures
Having a plan for emergencies can help mitigate risks and ensure a safe outcome.
Emergency Response Plan
In case of unexpected loss of control or a crash landing, immediately assess the situation and take appropriate action. Prioritize safety and avoid putting yourself or others at risk.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
When recovering a crashed drone, prioritize your safety. Inspect the drone for damage before attempting to power it on again.
Emergency Situations and Procedures
| Emergency Situation | Actions to Take | Safety Precautions | Post-Incident Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of Control | Attempt controlled descent; if impossible, cut power. | Avoid populated areas, assess surroundings. | Inspect for damage, assess cause of malfunction. |
| Crash Landing | Secure the area, inspect for injuries. | Approach cautiously, avoid touching damaged components. | Document damage, investigate cause, repair or replace as needed. |
| Battery Failure | Attempt emergency landing, prioritize safety. | Assess surroundings, ensure a safe landing zone. | Recharge or replace the battery. |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the essential components, flight techniques, and safety considerations involved. Remember that consistent practice, a commitment to safety, and ongoing learning are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. So, grab your controller, embrace the challenge, and explore the limitless possibilities of the aerial world.
Happy flying!
FAQ Corner
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance, and beginner-friendly flight modes.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (flight style and features used), and weather conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the fundamentals is crucial for safe and responsible flying, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety procedures.
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (e.g., ‘Beginner Mode’ or ‘Attitude Mode’) and carefully bring it down to a safe landing. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration frequency depends on usage. Regular calibration, at least once a month or after a crash, is recommended to maintain optimal performance and accuracy.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s aviation authority website or the website of your national aviation authority for specific drone regulations in your area.
